|
|
6年前 | |
|---|---|---|
| config | 6年前 | |
| debian | 6年前 | |
| docs | 6年前 | |
| html | 6年前 | |
| service | 6年前 | |
| src | 6年前 | |
| CHANGELOG.md | 6年前 | |
| Dockerfile | 6年前 | |
| Makefile | 6年前 | |
| README.md | 6年前 | |
| RELEASE.md | 6年前 | |
| drone.yml | 6年前 |
README.md
Radangel
Device: Kromek RadAngel
The Kromek RadAngel is an affordable CZT-based gamma-ray spectrometer device connecting via USB as a HID device.
RadAngel a small and portable gamma-ray spectrometer that can be utilised for educational purposes in teaching concepts of radiation as well as for training in the use of radiation sensors.
Its compact size and quick set-up time make it ideally suited for individual or small group projects, laboratory-based teaching, classroom demonstrations and field studies.
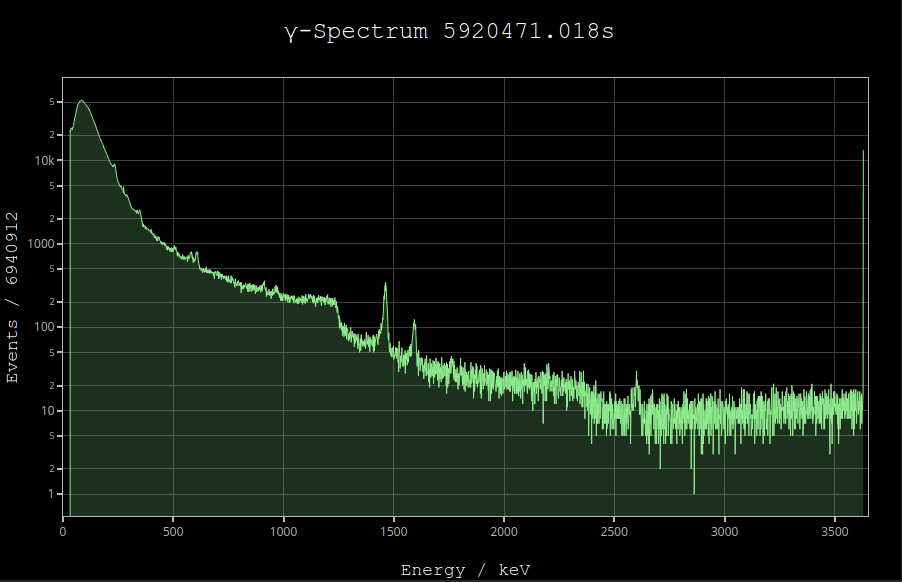
This instrument utilizes a Cadmium Zinc Telluride (CZT) solid state detector, which enables room temperature operation with excellent energy resolution (12 bits hence 4096 channels from ~30 keV to ~3 MeV). The unit is completely self-contained, with a built-in detector, amplifiers, power supply and communications. The digitized detector signals are sent to a PC via the mini-USB which also powers the unit, so no external supply is required.
Daemon: radangel
The radangel binary communicates with the RadAngel HID device (04d8:0100) via USB (hidapi-libusb) and uses threads (pthreads) to read events and push them in a queue, then pop them from the queue and write them into files.
To grant permissions to the USB device, the udev system can be employed:
echo 'SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="04d8", ATTR{idProduct}=="0100", MODE="0666"' | sudo tee /etc/udev/rules.d/60-kromek-radangel.rulessudo udevadm control --reload-rules && sudo udevadm trigger
Compiling the radangel binary for the linux operating system requires to install some dependencies in advance. To install the build dependencies on a Debian system the apt-get command can be used:
apt-get update && apt-get -y install build-essential libc6-dev libhidapi-dev
Then you have two options, to compile the binaryJust run make in the src directory or
run
makein thesrcdirectory orrun
gcc -std=gnu99 -Wall radangel.c -o radangel -pthread -lm -lhidapi-libusbin thesrcdirectory
The output of the radangel daemon consists of two files (time series and histogram):
events.tsveach line corresponds to one event with timestamp and channel (gamma-ray energy).stats.tsveach line corresponds to one channel and displays the number of occurance (histogram).
Running the binary with the appropriate arguments:
radangel --verbose --event events.tsv --stats stats.tsv
The daemon can be run as service with the radangel.service systemd file.
Web: service
The changes in the output files from radangel daemon can be streamed to the browser in realtime with the two systemd units datasrc.service
and websockify.service:
datasrc.servicesystemd unit employsinotailto monitor the output files and streams the changes withsocatinto a tcp socket.websockify.servicelaunches thewebsockifydaemon which provides the websocket endpoint behindnginxwebserver (seenginx-datasrc-location.conf) and translates between websocket and the plain tcp socket.
Again we need to satisfy the dependencies, e.g. on a Debian system with apt-get
apt-get update && apt-get -y install build-essential libc6-dev libssl-dev
To compile the websockify daemon just run make in the src/contrib directory.
The web interface itself uses Plotly.js to display the histogram of the channels in realtime by connecting to the websocket endpoint and provides a convenient user interface for exploring the details of the gamma-spectrum.